LED White Colors and CRI
Explanation of Cool White vs Warm White: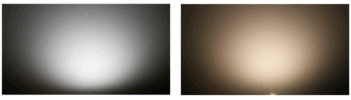 The pictures here show our typical Cool White (L) and Warm White (R) LED colors. Cool whites have a higher color temperature, and their dominant wavelengths are closer to the blue side of the spectrum. Warm whites have a lower color temperature, and their dominant wavelengths are closer to the red side of the spectrum.
The pictures here show our typical Cool White (L) and Warm White (R) LED colors. Cool whites have a higher color temperature, and their dominant wavelengths are closer to the blue side of the spectrum. Warm whites have a lower color temperature, and their dominant wavelengths are closer to the red side of the spectrum.
Cool White: The cool white is more stark, brighter, and has a more industrial tone. It is closer to a natural and neutral daylight white. Many customers like cool white for exterior applications, or where absolute brightness is important, like engine compartments.
Warm White: Warm white is a softer light, with a color meant to mimic an incandescent or halogen light. It is more pleasing to the eye, and works very well in interior applications because it tends to render richer colors better. Most people feel that our warm white looks just like an incandescent filament bulb. While Warm White LEDs are less bright than a Cool White of the same wattage, brightness is not a issue with Marinebeam Warm White LEDs, and they are at least as bright or brighter than their incandescent counterparts.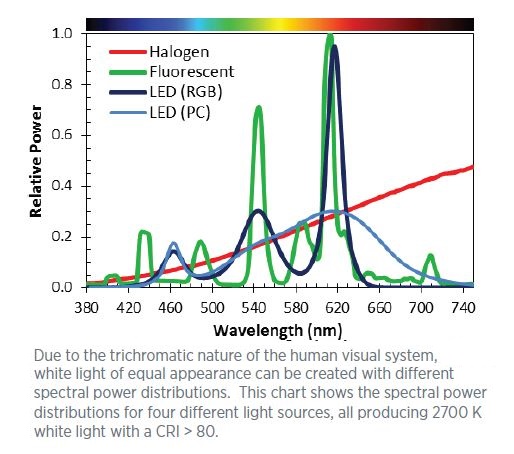
How does the LED make the white color?
White can be made two ways with LEDs. One way is to mix Red, Green and Blue (R,G,B) LEDs. Mixing all three colors will produce a white light, but the white it produces doesn't look much like the incandescent light we have become accustomed to. The other way to make white LED light is to use a blue LED emitter, and then coat the emitter with a phosphor and silicone. These Phosphor Coated (PC) LEDs make for the most pleasing light. We use PC LEDs, and it is the phosphor coating that makes the yellow dots that you see on the face of our LED bulbs.
The phosphors work by absorbing the blue wavelength light and then re-emitting that light in a new wavelength. The color emitted is based on the chemical elements that make up the phosphor coating. By adding different elements to the phosphor mix, a fuller-spectrum light can be produced. Unfortunately, as more elements are added to the mix, the conversion efficiency goes down. Most people are familiar with phosphors and their use with fluorescent lamps (the white powder on the inside of the tube is also a phosphor coating). With fluorescents, the cooler the light, the brighter the output. It is the same with LEDs.
The good news is that thanks to clean-room manufacturing and nano-phosphors, our warm white products are now plenty bright, and have the same or greater output than their warm white incandescent and fluorescent counterparts. Because of this advancing technology, you will now begin to see home lighting (screw-base Edison bulbs) transition away from compact-fluorescents (CFL) to LEDs, just like they did from filament bulbs to CFLs just a few years ago.
What is CRI?
CRI is Color Rendering Index. It is a measure of how accurately a light source renders actual colors when compared to how daylight (the li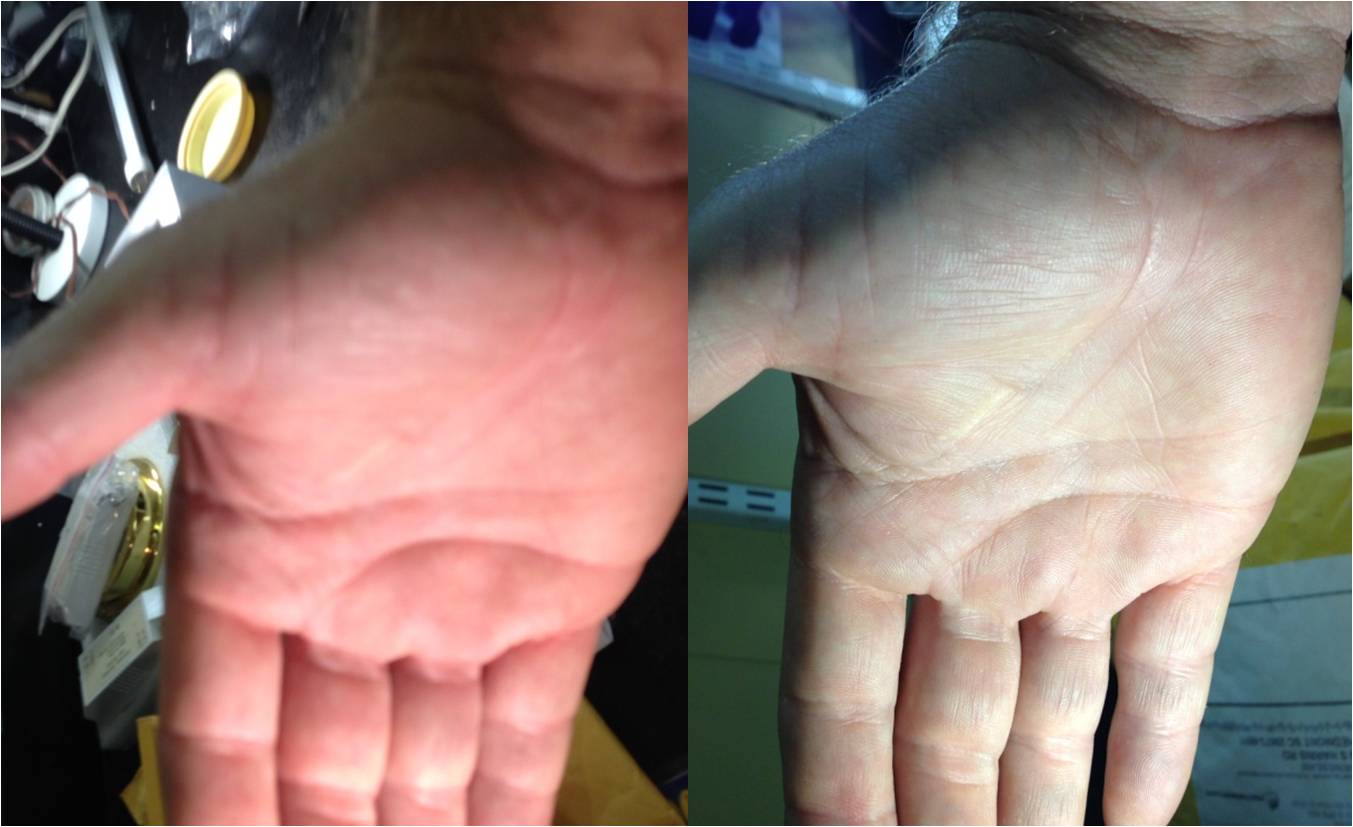 ght from our sun) renders those same colors. The sun scores a perfect 100 in CRI. Incandescents, like halogens, can score in the low 90's. Until relatively recently, Warm White LEDs were lucky to reach 70 CRI. But again, thanks to developing technology, all the Warm White LEDs from Marinebeam score at least 80 with most of our latest generation bulbs scoring more than 85 CRI. This is considered world-class color rendering at the moment.
ght from our sun) renders those same colors. The sun scores a perfect 100 in CRI. Incandescents, like halogens, can score in the low 90's. Until relatively recently, Warm White LEDs were lucky to reach 70 CRI. But again, thanks to developing technology, all the Warm White LEDs from Marinebeam score at least 80 with most of our latest generation bulbs scoring more than 85 CRI. This is considered world-class color rendering at the moment.
Color rendering is important, especially for boat interiors that have rich wood finishes, and for viewing food or other colorful items. While color temperature and CRI are not necessarily related, the CRI of our Warm White LEDs is much higher than our Cool White LEDs.
Take a look at the photo to the far right. This is from an internet bulb with 2900k color temp, but poor CRI. In contrast, compare that clammy washed-out look to the CRI from one of our bulbs on the left. Much warmer, with more red tones. Far better for food, woodwork, makeup, etc. too.
What is color temperature?
Color temperature is a way of measuring the color of a light source by comparing it to the color of the light emitted from an iron bar when heated to a specific temperature in degrees Kelvin (°K). When you think of metal being "white hot", it is reaching temperatures of 2000-7000°K. The color temperature of typical incandescent is between 2700-3100°K. Most fluorescent tubes are between 4100°K and 6500°K.
Our warm white LEDs are generally between 2700° and 3000°K. Our cool white LEDs are specified at between 6000° to 6500°K. We also offer some LED tubes in 4100°K.
